by Alana Hulme-Chambers, Samantha Clune, Jane Tomnay
International Journal for Equity in Health 2018;17:172. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-018-0888-8 (Open access)
Abstract
Background: Medical termination of pregnancy (MToP) is a safe and acceptable abortion option. Depending on country context, MToP can be administered by general practitioners and mid-level healthcare providers in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. Like other high-income countries, a range of social and structural barriers to MToP service provision exist in Australia. To counter some of these barriers, geographic decentralization of MToP was undertaken in rural Victoria, Australia, through training service providers about MToP to increase service delivery opportunities. The aim of this study was to investigate the factors that enabled and challenged the decentralization process.
Methods: Face-to-face and telephone interviews were undertaken between April and June 2016 with a purposeful sample of six training providers and 13 general practitioners (GP) and nurse training participants. Study participants were asked about their perceptions of motivations, enablers and challenges to MToP provision. A published conceptual framework of synergies between decentralization and service delivery was used to analyse the study findings.
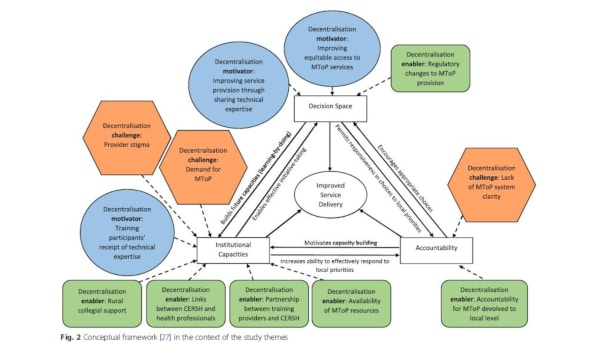
Results: Three key themes emerged from the study findings. First, the effort to decentralize MToP was primarily supported by motivations related to making service access more equitable as well as the willingness of training providers to devolve their informal power, in the form of MToP medical expertise, to training participants. Next, the enablers for MToP decentralization included changes in the regulatory environment relating to decriminalization of abortion and availability of required medication, formation of partnerships to deliver training, provision of MToP clinical resources and local collegial support. Finally, challenges to MToP decentralization were few but significant. These included a lack of a state-wide strategy for service provision, provider concerns about coping with service demand, and provider stigma in the form of perceived negative community or collegial attitudes. These were significant enough to create caution for GPs and nurses considering service provision.
Conclusions: Decentralization concepts offer an innovative way for reframing and tackling issues associated with improving MToP service delivery. There is scope for more research about MToP decentralization in other country contexts. These findings are important for informing future rural MToP service expansion efforts that improve equity in service access.



